Pros and Cons of Different Business Structures in Australia
For any person to do business successfully in Australia, one of the most important things is to set up the business under the correct business structure.
Distinct Business Solutions has put together an easy to use guide, complete with an explanation of each business structure as well as the pros and cons associated with each.
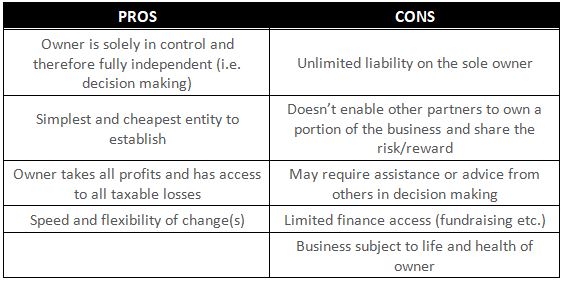
Sole Trader Business Structure
Setting up of this business structure is relatively simple and inexpensive as it involves very limited legal and tax regulations. The profit of a sole trader business structure is reported in the individual tax return of the owner and income tax is paid based on their individual tax rates.
Drawbacks of this structure include that fact that you are personally liable for all debts and liabilities of your business. In sole trader business structure, the owner, alone, responsible is for all business operations. This business structure provides no personal asset protection. While cheap and easy to set up, a sole trader business structure could prove to be quite risky.
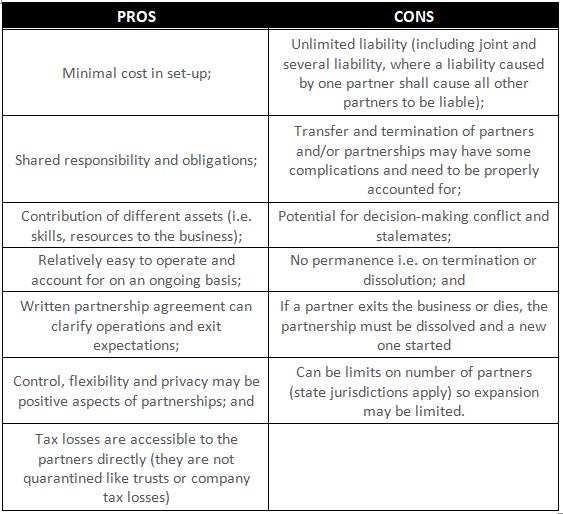
Partnership Business Structure
Like the name suggests, the partnership involves two or more people in managing and operating a business with a common view to profit. A partnership has its own ABN, Tax File Number, GST registration and it will lodge its own tax return each year. Ownership can be equal ((i.e. 50/50) or different (i.e. one partner may have 40% interest and another 60%). Whilst a partnership must lodge a tax return, the business does not pay income tax as the profits (or losses) are distributed to the partners in accordance with their ownership percentages.
As with a sole trader business structure, in a Partnership structure, partners are personally liable for all debts and liabilities of the business. This business structure provides no personal asset protection.
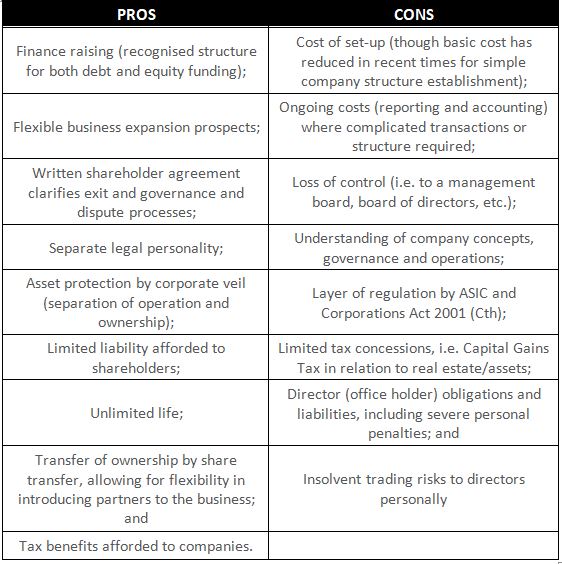
Company Business Structure
A company is considered a separate legal entity under Australian law. When a person forms a company, it is created and registered with ASIC (Australian Securities & Investments Commission), the government authority who regulates them.
The company must have 1 or more directors that are responsible for the operations of the company, as well as a Secretary and Public Officer. The Directors are responsible to the shareholders.
A company pays tax at its relevant company tax rate. Shareholders then receive the benefit of a franking credit for this tax paid when paying out profits in the form of dividends. In addition to lodging a company tax return, the shareholders also need to lodge their own individual tax return.
A company has the advantage of limited liability, meaning that the debts of company are those of the company itself and not of the directors and shareholders, unless a director’s guarantee is signed or negligence on their part has been proven.
Whilst it is a more costly business structure, a company provides many benefits to shareholders that other business structures do not, especially in the case of personal asset protection.
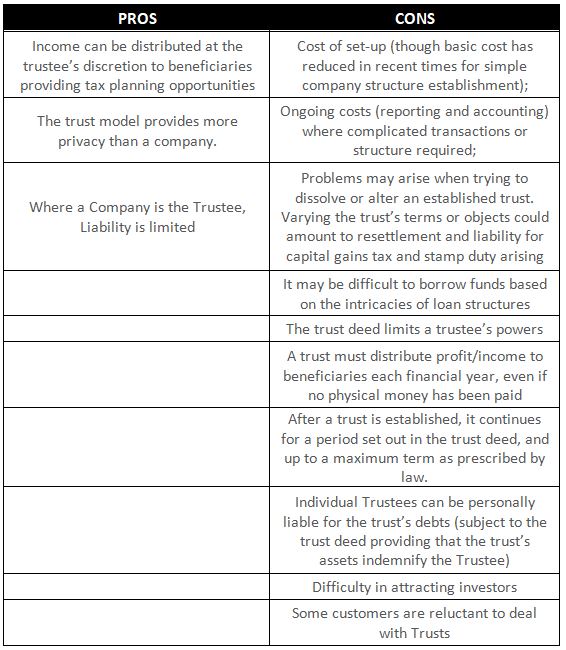
Trust Business Structure
Whilst there a few types of trusts, in this article we focus on Discretionary trusts, also known as family trusts.
Trusts are a very popular structure for owning and operating businesses, particularly in family units.
Trust Popularity for business owners relates to benefits associated with asset protection and income distribution, among other things.
All Trusts essentially have the same structure, with minor variations to their rules (i.e. the trust deed) to distinguish the trust and allow it to perform different functions.
Unlike a sole trader structure, a trust business structure is more complex to set up. In this setup, a person or company will become a trustee for the assets of a beneficiary who will conduct and do business on the behalf of the beneficiary.
When choosing your business structure, it is recommended that you seek the advice of a professional accounting firm to ensure that you choose the correct structure for you and your circumstances.
Find out more about Distinct Business Solutions’ Business Coaching Services
Arrange a consultation, or Contact Us
Any advice in this blog is general in nature and is intended for information purposes only. For personalised advice please contact your accountant.